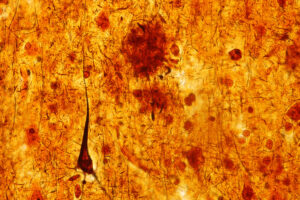
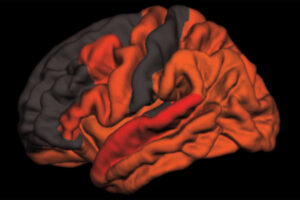
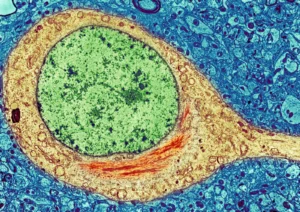
A drug under consideration by the Food and Drug Administration for multiple sclerosis has shown superiority in terms of gastrointestinal tolerability over its comparator. But while analysts said the drug will likely win FDA approval, it is uncertain if the latest data will drive significant uptake, especially with the comparator’s anticipated availability as a generic.
Biogen, Alkermes MS drug bests Biogen’s soon-to-be-generic blockbuster in Phase III study (Links to an external site)