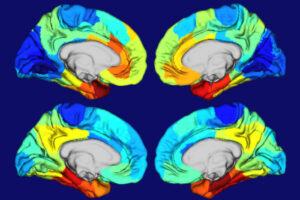
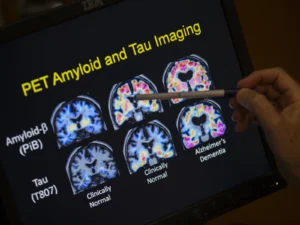
ST. LOUIS — Joe knew something was terribly wrong when his wife, an energetic nurse and mother of three, became forgetful in her early 60s. Four years ago, Lynn was diagnosed with dementia but decided against having a spinal tap that would have shown whether the cause was Alzheimer’s disease.
Is it Alzheimer’s? Families want to know, and blood tests may offer answers. (Links to an external site)