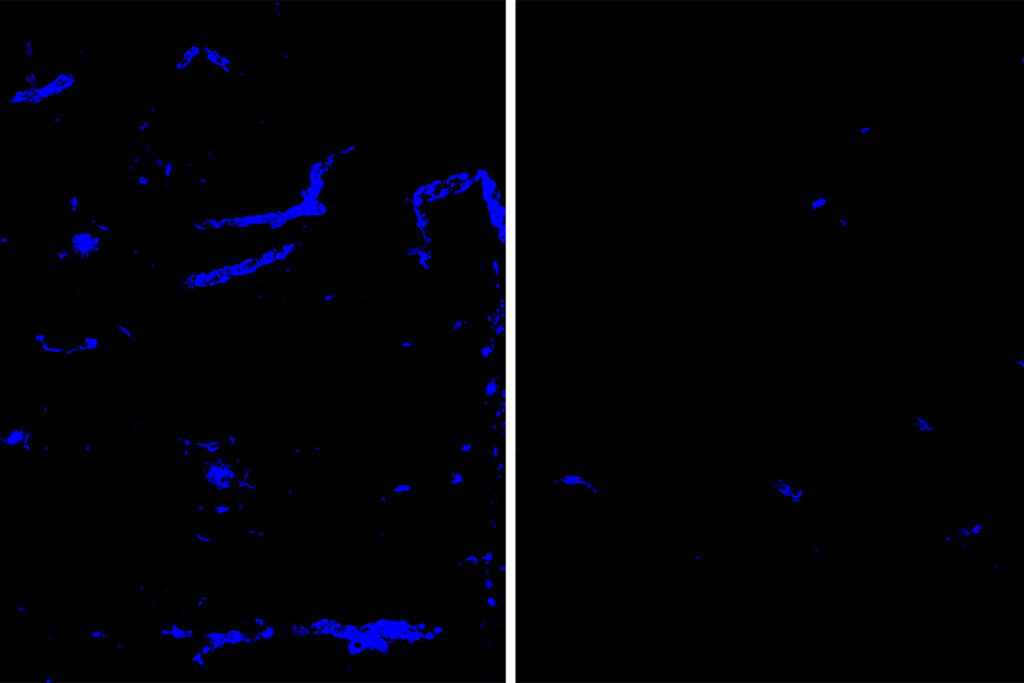
As people age, a normal brain protein known as amyloid beta often starts to collect into harmful amyloid plaques in the brain. Such plaques can be the first step on the path to Alzheimer’s dementia. When they form around blood vessels in the brain, a condition known as cerebral amyloid angiopathy, the plaques also raise the risk of strokes.
Protein linked to Alzheimer’s, strokes cleared from brain blood vessels
View Content